A new paper published in the journal Environmental Research Letters presents the first multi-model analysis of the potential effects of IRA on the power sector, considering such uncertainties.
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) is considered a pivotal federal climate legislation in the United States, holding potential to lower greenhouse gas emissions, reduce energy costs, and address inequalities within the energy system. However, the complexity and broad scope of the IRA raise uncertainties regarding its impact on the energy system and related emissions.
“IRA is assessed to have the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, lower energy costs, and address inequalities in the energy system,” said KAIST visiting professor Haewon McJeon, who coauthored the study. “This study is the first multi-model analysis to demonstrate the potential effects of IRA on the power sector.”
This study indicates that the IRA tends to reduce coal and natural gas generation while increasing the share of low-emission power sources. The impact of IRA closures affects coal power plants more than natural gas ones, while low-emission sources like renewables, nuclear, and CCS-equipped generation expand. The research suggests that IRA drives faster and deeper emissions reductions in the power sector compared to other sectors. The findings show that carbon dioxide emissions in the power sector are reduced by 47-83% from 2005 levels by 2030, further decreasing by an additional 66-87% by 2035.
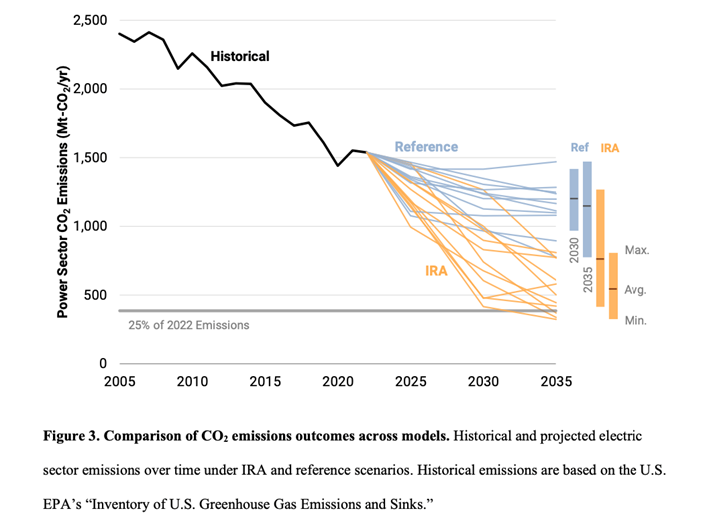
This analysis sheds light on the potential impacts of the United States’ Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) on the U.S. power sector, highlighting its role in driving emissions reductions and shaping the energy landscape. This study indicates that power generation holds the largest share in U.S. reductions, according to models, and they unanimously agree. Also, there’s a consensus that coal-fired generation needs to retire relatively quickly. However, there are varying predictions among models regarding the proportions of solar, wind, and nuclear, indicating the need for further research. It underscores various uncertainties such as deployment challenges, policy effectiveness, technological changes, and model differences that can influence the impact of IRA.
Research conducted using a single model comes with considerable uncertainties, emphasizing the need for comparing multiple models in this study. In this regard, the ongoing role of K-EMF (Korea Energy Modeling Forum) holds great importance. The future research of K-EMF can also address similar policies in Korea. Moreover, such studies can provide valuable insights for developing policies tailored to the situation in Korea.
Read the full paper here: https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ad0d3b
한국어 요약
인플레이션 감축법안 (IRA) 이 2022년에 발효된 이후 전력 부문에 미치는 영향
2022년 발효된 인플레이션 감축법안 (IRA) 은 미국에서 가장 중요한 연방 기후법안으로 간주되며 온실가스 배출을 감소시키고 에너지 비용을 낮추며 에너지 시스템의 불평등을 해결할 잠재력이 있다고 평가된다. 그러나 IRA의 복잡성과 폭넓은 범위로 인해 에너지 시스템 및 관련 배출에 미치는 영향이 불확실하다.
카이스트 녹색성장지속가능대학원 전해원 방문교수를 포함한 연구진은 이런 불확실성을 고려하여 IRA가 전력 부문에 미치는 잠재적인 영향에 대한 최초의 다중 모델 분석을 Environmental Research Letters 저널에 출간하였다.
이 연구는 단일 모델이 가지는 큰 불확실성을 줄이기 위해 여러 모델의 비교가 중요하다는 것을 시사한다. 그런 의미에서 한국에서 현재 진행중인 한국 에너지모델링포럼 (K-EMF) 의 역할에 시사하는 점이 크다.
