High-resolution land system data is crucial for understanding and planning effective climate mitigation strategies at global scales.
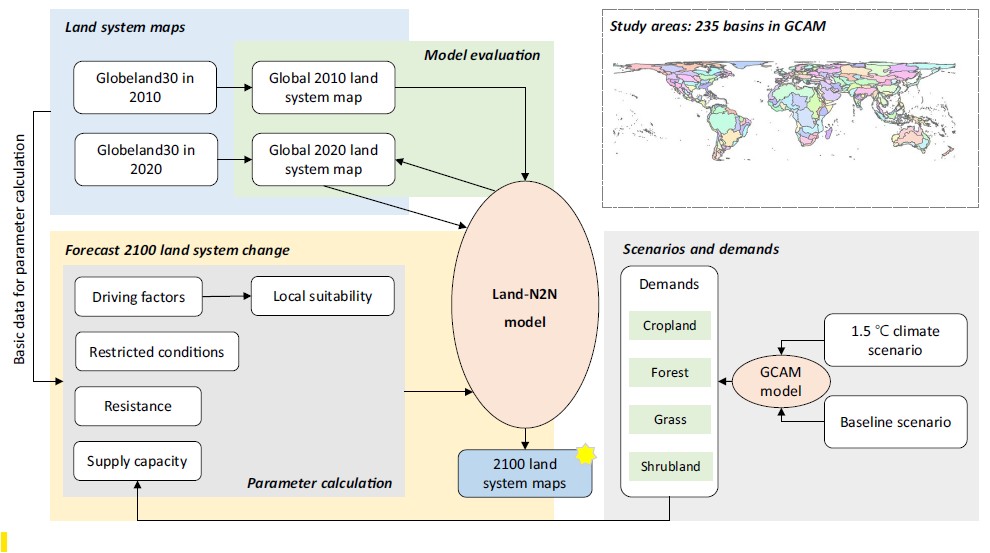
This data-focused paper, published in Scientific Data, presents global land system maps from 2010 through 2100 at a detailed 1 km spatial resolution under baseline and ambitious 1.5°C climate scenarios.
The dataset was developed by harmonizing outputs from the Global Change Analysis Model (GCAM) with an improved CLUMondo land-change model. This integration enables detailed spatial analysis of how global land systems could evolve in response to climate policies, providing critical support for sustainable land management and mitigation planning.
“As efforts to limit climate change intensify, higher resolution data is becoming increasingly important for a better understanding of mitigation dynamics,” said Prof. Haewon McJeon of KAIST Graduate School of Green Growth and Sustainability. “This study demonstrates a new methodology for harmonizing integrated assessment models with high-resolution land data models, which will help illuminate optimal paths for the sustainable mitigation of climate change.”
The dataset expands on our previous work published in Nature Climate Change, titled “Meeting the global 1.5-degree goal could result in large-scale heterogeneous loss in croplands”, and serves as a valuable resource for climate and sustainability research.
[paper link]: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-025-04991-0
한국어 요약
1.5°C 기후 목표 달성을 위한 1km 해상도의 전지구 토지 시스템 지도 구축
고해상도의 전 지구적 토지 시스템 데이터는 기후변화 대응을 위한 효과적인 정책 수립과 이행 과정에서 매우 중요한 자료입니다.데이터 전문 국제 학술지 『Scientific Data』에 게재된본 연구는 전 지구 토지 시스템의 변화를 2010년부터 2100년까지 1km의 높은 해상도로 구축한 데이터셋을 제공합니다. 이 데이터셋은 현재와 같은 정책을 유지하는 기준 시나리오와 지구 평균 기온 상승을 1.5°C로 제한하는 적극적인 기후대응 시나리오 두 가지로 구성되어 있습니다.
본 연구는 통합평가모델인 GCAM(Global Change Analysis Model)의 결과를 토지이용 변화를 정밀하게 시뮬레이션할 수 있는 CLUMondo 모델과 통합하여 개발되었습니다. 이렇게 개발된 데이터는 기후 정책에 따라 전 지구 토지 시스템이 어떻게 변화할지 상세한 공간 분석을 가능하게 하여 지속가능한 토지 관리 및 기후변화 완화 계획 수립에 필수적인 기초 자료로 활용될 수 있습니다.
KAIST 녹색성장지속가능대학원의 전해원 교수는 “기후변화 대응이 본격화될수록 고해상도 데이터의 중요성이 더욱 커지고 있다”며, “본 연구는 통합평가모델과 고해상도 토지 데이터 모델을 성공적으로 통합한 새로운 방법론을 제시하여 지속가능한 기후변화 대응을 위한 최적의 경로를 만들어 내는데 기여할 것”이라고 설명했습니다.
이번 데이터셋은 국제 학술지 『Nature Climate Change』에 발표한 논문(“Meeting the global 1.5-degree goal could result in large-scale heterogeneous loss in croplands”)의 데이터를 발전시킨 것이며, 향후 다양한 기후 및 지속가능성 관련 연구에 중요한 자료로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대됩니다.
