A new study proposes ways to cut global transportation emissions, a key area for mitigating climate change. The transportation sector is responsible for 20% of global carbon emissions, with aviation and maritime being especially challenging to mitigate due to limited clean technology options.
A new study published in Environmental Research Letters assess the deployment of Direct Air Capture and Carbon Storage (DACCS) technology at the provincial level needed to achieve China’s carbon neutrality goal, emphasizing the importance of regional strategies. This study is the first to evaluate how DACCS technology can be effectively implemented across all Chinese provinces using an integrated assessment model, providing valuable insights for both national and regional governments as they plan and prepare for the net-zero future.
Key Points of the Study
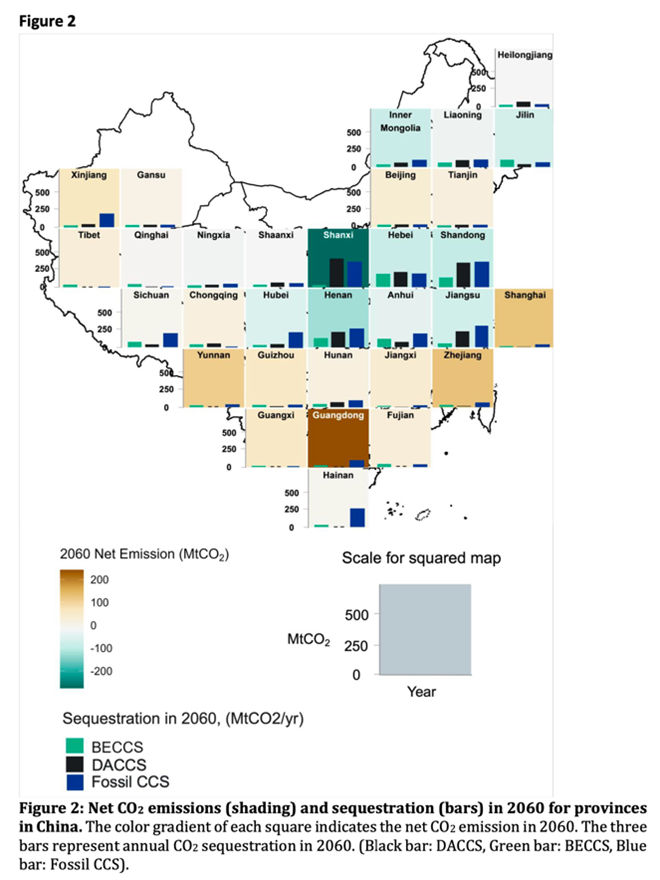
Tailored Decarbonization Pathways by Province: Each province in China has different geological conditions, leading to variations in decarbonization pathways for achieving carbon neutrality. The study shows that the deployment of BECCS and DACCS can differ depending on the geological CO2 storage resource availability in each province.
The Need for Renewable Energy: Large-scale deployment of DACCS technology requires substantial electricity usage, which is analyzed to necessitate approximately 635 GW of additional renewable energy capacity nationwide by 2060. The study also suggests that excess electricity in some provinces could be transmitted to other regions, considering the differences in power supply and demand across provinces.
Economic Efficiency of DACCS: DACCS is identified as an important technology that can offset the reduction in BECCS deployment, especially when biomass supply is limited, with significant potential to reduce transition and policy costs.
Implications
This study highlights the crucial role DACCS technology can play in achieving China’s carbon neutrality goal. International research and development collaboration, as well as global cooperation in carbon markets, are essential for the successful implementation and dissemination of DACCS technology. Also, establishing and preparing DACCS hubs will lay the foundation for China to contribute to global climate goals.
“China’s carbon emissions have been growing rapidly,” said Prof. Haewon McJeon of KAIST Graduate School of Green Growth and Sustainability, who coauthored the study. “We need to better understand how CO2 removal technologies in China can be effectively utilized to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060”.
Read the full paper: https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ad77e7
제한된 바이오에너지 공급 하에서 중국의 기후 중립 목표 달성을 위한 성 단위의 직접 공기 포집 평가
국제학술지 Environmental Research Letters에 발표된 연구에 따르면 중국의 탄소 중립 목표를 달성하기 위한 지방 단위에서의 DACCS(직접 공기 포집 및 탄소 저장) 기술 배치 전략을 심층적으로 분석하여, 지역별 전략의 중요성을 강조한다. KAIST 녹색성장지속가능대학원 전해원 교수가 참여한 이 연구는 GCAM-China 모델을 통해 중국의 각 성 단위별로 DACCS 기술을 효과적으로 구현하는 방안을 최초로 평가하였으며, 이를 통해 국가 및 지방 정부가 DACCS 허브를 계획하고 준비하는 데 중요한 시사점을 제공한다.
연구의 핵심 포인트
지방별 맞춤형 탈탄소 경로
중국의 각 지방은 서로 다른 지질학적 조건을 가지고 있어, 탄소 중립을 위한 탈탄소 경로도 상이할 수밖에 없음.
연구는 각 지방의 지질학적 이산화탄소 저장 자원 활용 가능성에 따라 BECCS와 DACCS 배치가 달라질 수 있음을 보여줌.
재생 가능 에너지의 필요성
DACCS 기술을 대규모로 배치하기 위해서는 상당한 전력 사용이 요구되며, 이를 위해 2060년까지 전국적으로 약 635GW의 추가 재생 가능 전력 생산 용량이 필요할 것으로 분석됨.
지역 간 전력 수급 차이를 고려하여 일부 지방에서는 초과 전력을 다른 지방으로 공급하는 전략도 고려됨.
DACCS의 경제적 효율성
- DACCS는 특히 바이오에너지 공급이 제한된 경우 BECCS 배치의 감소를 보완할 수 있는 중요한 기술로, 전환 비용과 정책 비용을 크게 줄일 수 있는 잠재력이 있음.
시사점
이번 연구는 DACCS 기술이 중국의 탄소 중립 목표 달성에 핵심적인 역할을 할 수 있음을 강조한다. 그러나 이를 효과적으로 구현하기 위해서는 신중한 계획과 더불어 국제적 협력이 필수적이다. 특히, DACCS 허브의 계획 및 준비를 통해 중국이 글로벌 기후 목표 달성에 기여할 수 있는 기반을 마련해야 한다.
이 연구에 참여한 KAIST 녹색성장지속가능대학원 전해원 교수는 “중국의 탄소 배출량이 급격히 증가하고 있다”며 “중국이 2060년까지 탄소중립을 달성하는데 탄소포집 기술이 어떤 기여를 할 수 있을지 더 많은 분석이 필요하다.”라고 전하며 이 연구의 중요성을 강조한다.
